ROS 进阶学习笔记(16):ROS导航1:关于Costmap_2d Package (代价地图包)
=== 关于Costmap_2d Package ===
wiki page: http://wiki.ros.org/costmap_2d
=== 我遇到的问题是 obstacle layer的刷新频率太低 ===
costmap_2d包下的所有类文档:http://docs.ros.org/hydro/api/costmap_2d/html/annotated.html
其中,值得注意滴是 costmap_2d::ObservationBuffer 这个类,这个类会被 costmap_2d::ObstacleLayer 调用,obstacle_layer.cpp(Link of source code)
其中,observation_keep_time和expected_update_rate应该是决定刷新频率的参数,其默认是0.0
但实际nav_test.py运行时,这个参数是1.0, 我用rosparam set改成0.0了也没实际效果。
I’m trying to solve this issue….
=== 我学这个包的时候,尽量总结wiki page上的内容如下:===
所属Stack: navigation
关于这个包在 ROS Navigation 框架中的位置,参见: ROS探索总结(十三)——导航与定位框架
Sammary:
1. 实现2D cost map
2. 输入: sensor data
3. 生成: 占用格数据,inflates cost in a 2D costmap.
4. 支持 基于map_server的一个costmap的初始化,
支持 基于rolling window的costmaps,
支持 基于参数的,对一个传感器topics的配置的订阅。
wiki web page上有图(图片地址见下),说明神马是cost map.
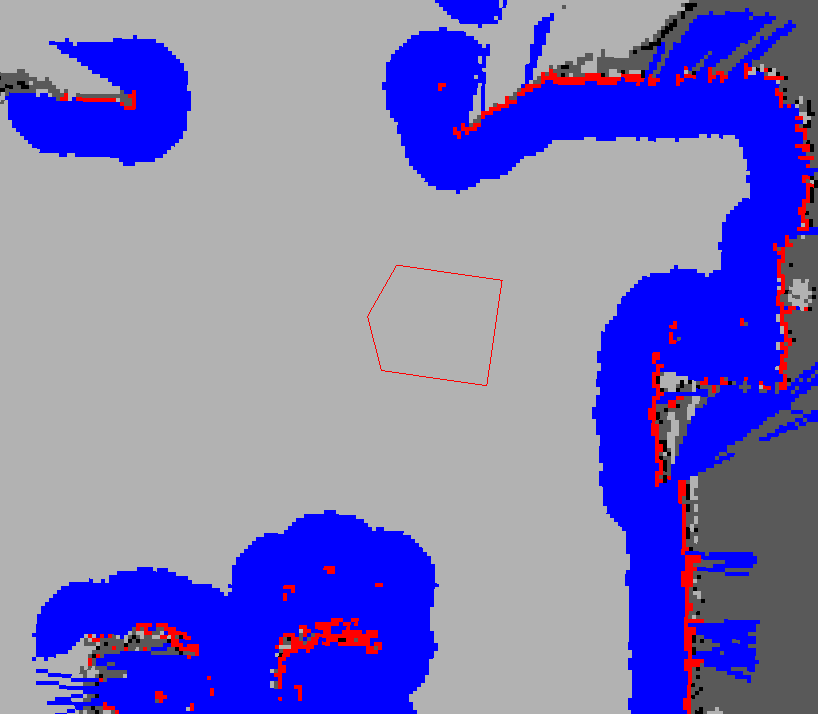
图片地址:http://wiki.ros.org/costmap_2d?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=costmap_rviz.png
红色cell是costmap 上的障碍,蓝色是通过机器人半径膨胀出的障碍,红色多边形是机器人
footprint即垂直投影。要不碰撞,footprint不能和红色cell有交叉,并且地,机器人中心不能与蓝色
cell有交叉。
costmap_2d这个包提供了一个可以配置的结构。这个结构处理关于机器人在一个occupancy grid(占
用网格)里,应该导航到哪里的信息。costmap 使用了传感器数据和来自固态地图的信息,通过
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS对象(Object),来保存和更新关于障碍物的信息。
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS对象,提供了一个purely 2D接口给它的用户,这意味着queries about
obstacles can only be made in columns(列). 例如,一张桌子和一双鞋在XY平面上的同一个地方,但
有不同的Z高度,这会让在costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS对象中对应的cell有相同的cost值(译者注:看来
,cost可翻译成“占用”)。这种设计就是为了便于planar spaces中的路径规划。(注:看来
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS对象很重要)
Hydro版本中,the underlying(已有的) methods used to write data to the costmap is fully
configurable. Each bit of functionality exists in a layer. 举个例子:静态地图在第一层,
obstacles 是另一层。默认地,the obstacle layer maintains information three dimentionally.(
这里用的是voxel_grid包,关于voxel_grid,它提供了一个关于efficient 3D voxel grid的实现。体素
或立体像素(voxel)。The occupancy grid can support 3 different representations for the state
of a cell: marked, free, or unknown.)Maintaining 3D 障碍数据使得这些层可以更智能地处理
marking and clearing.
主要的接口就是costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS对象,它Maintain了很多有关ROS的功能。
1. 包括,costmap_2d::LayeredCostmap类,用来keep track of each of the layers。
2. 每个层是在Costmap2DROS中,用pluginlib来实例化,并加入到LayeredCostmap类的对象中(Each
layer is instantiated in the Costmap2DROS using pluginlib(http://wiki.ros.org/pluginlib)
and is added to the LayeredCostmap. )这些层们可能独立地被编译,允许通过C++interface来对
costmap任意的改变。
3. 还有一个costmap_2d::Costmap2D类,implements the basic data structure for storing and
accessing the two dimensional costmap. 实现了基础的数据结构,用来存储和读取2D costmap的数据
结构。
The main interface is costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS which maintains much of the ROS related
functionality. It contains a costmap_2d::LayeredCostmap which is used to keep track of each
of the layers. Each layer is instantiated in the Costmap2DROS using pluginlib and is added
to the LayeredCostmap. The layers themselves may be compiled individually, allowing
arbitrary changes to the costmap to be made through the C++ interface. The
costmap_2d::Costmap2D class implements the basic data structure for storing and accessing
the two dimensional costmap.
(看到这里我有点晕,大意就是costmap实例化了就成了Layer, 通过Costmap2DROS类来实例化,放在
了以LayeredCostmap类下的对象里,由LayeredCostmap管理。)
下面就讲how the costmap updates the occupancy grid. 带有去往不同layer工作机制介绍页面的
链接。
【标记和清除机制】
The costmap automatically subscribes to sensors topics over ROS and updates itself
accordingly. Each sensor is used to either mark (insert obstacle information into the
costmap), clear (remove obstacle information from the costmap), or both. A marking
operation is just an index into an array to change the cost of a cell. 但是,清除机制就包含
通过网格的raytracing(光线追踪).这个网格源自每个由传感器报告上来的观察。如果一个3D数据结构
用来存储obstacle 信息,在put them into costmap时,我们要把它的每一列数据重新映射到2D。
【Occupied, Free, and Unkown空间】
每个方格有255个值,8位
每个方格在这种数据结构下,有三种状态:free, occupied, unknown
每个状态都有其对应的cost value.
有些列有相当数量的occupied cells,就被分配了一个 costmap_2d::LETHAL_OBSTACLE cost。
有些列有相当数量的unknown cells,就被分配了一个 costmap_2d::NO_INFORMATION cost。
有些列有相当数量的occupied cells,就被分配了一个 costmap_2d::FREE_SPACE cost。
【地图更新】
执行更新,At the rate specified by the update_frequency 参数。costmap的占用数据结构
(occupancy structure)要执行更新。并且这个数据结构要映射到costmap,where 合适的cost value要
分配,按照occupied, free and unkown的阈值来。这个进行完了,每个障碍的膨胀就要在每个cell上进
行,在 costmap_2d::LETHAL_OBSTACLE cost 的指导下进行。按照用户指定的半径进行繁殖。具体要在
下面inflation process中介绍。
【tf坐标变换】
假设所有的变换都是在 global_frame参数和robot_base_frame指定的 坐标系 之间变换。
transfor_tolerance 参数设置了这些变换之间的最大延迟量(latency),没有够快就会被
navigation stack叫停机器人。
【Inflation膨胀】
图片:http://wiki.ros.org/costmap_2d?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=costmapspec.png
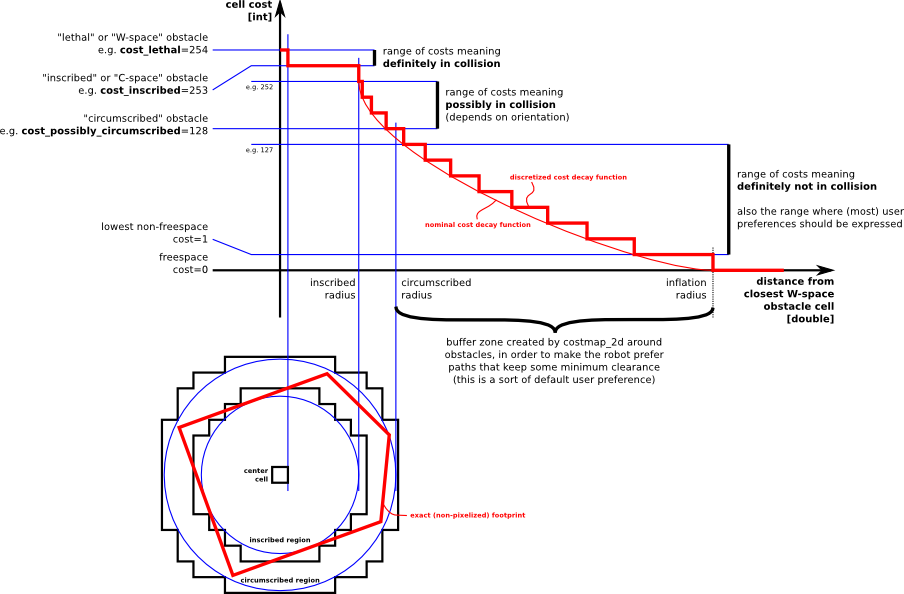
定义了5个象征符号for costmap values
1. Lethal - 致命的
2. Inscribed - 内切的
3. Possibly circumscribed - 可能外切的
the true value is influenced by both the inscribed_radius and inflation_radius parameters
4. Freespace - 0=costvalue, 机器人可去的地方
5. Unknown - No info
6. 其他介于free 和 possibly circumscribed之间的。就看它的距离和用户定义的decay函数了。
这些定义背后的原理就是: 我们把有些东西留给了对路径规划器的实现方式上。是不是要考虑实际的
footprint, 仍然给他们了足够的信息让他们拿来生成tracing out the footprint的cost.
总结: 在ROS的导航中,costmap_2d这个包主要负责根据传感器的信息建立和更新二维或三维的地图。ROS的地图(costmap)采用网格(grid)的形式,每个网格的值从0~255,分为三种状态:占用(有障碍物)、无用(空闲的)、未知。
上图共分为五个部分:(下面的红色框图是机器人的轮廓,旁边的黑框是上图的映射位置)
(1) Lethal(致命的):机器人的中心与该网格的中心重合,此时机器人必然与障碍物冲突。
(2) Inscribed(内切):网格的外切圆与机器人的轮廓内切,此时机器人也必然与障碍物冲突。
(3) Possibly circumscribed(外切):网格的外切圆与机器人的轮廓外切,此时机器人相当于靠在障碍物附近,所以不一定冲突。
(4) Freespace(自由空间):没有障碍物的空间。
(5) Unknown(未知):未知的空间。
【地图类型】
生成costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS有2中方式,
- 第一种是:seed it with a user-generated static map,走到哪里蔽障就是。
- 第二种:give it a width and height and to set the rolling_window parameter to be true。rolling_window parameter让机器人处在costmap正中间,当机器人走太远时,放下障碍物。这种一般用在计程计调整架构(odometric coordinate frame)中,这种架构里,机器人只关心在一个local area里的障碍物。这里涉及到的rolling_window参数是用来设置在机器人移动过程中是否需要滚动窗口,以保持机器人处于中心位置。
【组件及API】
本节介绍编程时具体如何建立上述的对象,参数配置说明,层定义等.
1. 关于 Costmap2DROS 类
这 costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS 对象是一个对 costmap_2d::Costmap2D 对象的Wrapper封装器,把它的功能暴露成一个C++ ROS Wrapper . 它是在ROS的命名空间里(这里我们在下面就以~
一个创建 costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS 对象的代码例子如下:
——————-Code:—————–
#include <tf/transform_listener.h>
#include <costmap_2d/costmap_2d_ros.h>
…
…
tf::TransformListener tf_lsnr(ros::Duration(10));
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS costmap_obj(“my_costmap”,tf);
——————————————–
1.1 关于 ROS API
关于老的参数的注意事项:
很多参数都相对hydro版本以前的版本变化了,为了更大化参数配置的自由度。那些老参数的命名空间还是会work, 没有必要reconfigure你的robot. 但是,当costmap代码运行时,首先发生的是,参数们将会被从他们老的地方移除,然后放到the new locations with plugins properly added.
1.2 Costmap2DROS 对象要收听的主题:
~
Specification for the footprint of the robot. This replaces the previous parameter specification of the footprint.
1.3 Costmap2DROS 对象要发布的主题:
~
The values in the costmap
~
The values of the updated area of the costmap
~
Optionally advertised when the underlying occupancy grid uses voxels and the user requests the voxel grid be published.
1.4 **参数配置说明**
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS 对象是可以高度参数配置化的对象,参数涉及到的模块有:坐标系、tf, rate节拍, 机器人的解析,and, 地图管理。
==坐标系和tf参数==
~
The global frame for the costmap to operate in.
定义costmap操作时,所参考的全局地图,默认是/map,String类型
~
The name of the frame for the base link of the robot.
机器人基础坐标系
~
Specifies the delay in transform (tf) data that is tolerable in seconds.
定义了tf数据可以容忍(tolerable)延迟到达的时间.
This parameter serves as a safeguard to losing a link in the tf tree while still allowing an amount of latency the user is comfortable with to exist in the system. For example, a transform being 0.2 seconds out-of-date may be tolerable, but a transform being 8 seconds out of date is not. If the tf transform between the coordinate frames specified by the global_frame and robot_base_frame parameters is transform_tolerance seconds older than ros::Time::now(), then the navigation stack will stop the robot.
如果一个tf变换超过了tolerance限定的时间,机器人将被停止。
==rate节拍参数==
~
The frequency in Hz for the map to be updated.
地图更新速度,Hz
~
The frequency in Hz for the map to be publish display information.
地图发布到显示信息的频率
== 地图管理参数 ==
~
Whether or not to use a rolling window version of the costmap.
是不是要用滚动窗口模式(机器人不动)来查看地图
If the static_map parameter is set to true, this parameter must be set to false. 如果static_map参数设置为1,这个参数就要设置为0
== 下面这些参数是可以被有些层重写的,名字上讲,就是the static map层 ==
~
The width of the map in meters.
~
The height of the map in meters.
~
The resolution of the map in meters/cell.
~
The x origin of the map in the global frame in meters.
~
The y origin of the map in the global frame in meters.
“width,” “height,” 和"resolution" 设置设置costmap代价地图长(米)、高(米)和分辨率(米/格)。分辨率可以设置的与静态地图不同,但是一般情况下两者是相同的。
**以上就是costmap参数配置说明**这些参数是存放在 local_costmap_params.yaml 文件中的
1.5 tf变换要求
(value of global_frame parameter) → (value of robot_base_frame parameter)
Usually provided by a node responsible for odometry or localization such as amcl(link).
通常都是由负责odometry或者定位的node,比如amcl node,来提供这个tr 变换。
1.6 C++ API
For C++ level API documentation on the costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS class, please see the following page:Costmap2DROS C++ API
2. 关于层 Layer 的 Specification 指派/定义
- Static Map Layer - The static map layer represents a largely unchanging portion of the costmap, like those generated by SLAM.
- Obstacle Map Layer - The obstacle layer tracks the obstacles as read by the sensor data. The ObstacleCostmapPlugin marks and raytraces obstacles in two dimensions, while theVoxelCostmapPlugin does so in three dimensions.
- Inflation Layer - The inflation layer is an optimization that adds new values around lethal obstacles (i.e. inflates the obstacles) in order to make the costmap represent the configuration space of the robot.
- Other Layers - Other layers can be implemented and used in the costmap via pluginlib. Any additional plugins are welcomed to be listed and linked to below.
以上就是对wiki/costmap_2D官方页面的不准确翻译,纯当学习。下面我想分享一个 古-月 的博客《ROS探索总结(十九)–如何配置机器人的导航功能》中有关cost_map代价地图配置的内容:
古月的博客:代价地图的配置 (local_costmap)& (global_costmap)
导航功能包使用两种代价地图存储周围环境中的障碍信息,一种用于全局路径规划,一种用于本地路径规划和实时避障。两种代价地图需要使用一些共同和独立的配置文件:通用配置文件,全局规划配置文件,本地规划配置文件。以下将详细讲解这三种配置文件:
(1)通用配置文件(Common Configuration (local_costmap) &(global_costmap))
代价地图用来存储周围环境的障碍信息,其中需要注明地图关注的机器人传感器消息,以便于地图信息进行更行。针对两种代价地图通用的配置选项,创建名为costmap_common_params.yaml的配置文件:
[html] view plain copy 
- obstacle_range: 2.5
- raytrace_range: 3.0
- footprint: [[x0, y0], [x1, y1], … [xn, yn]]
- #robot_radius: ir_of_robot
- inflation_radius: 0.55
- observation_sources: laser_scan_sensor point_cloud_sensor
- laser_scan_sensor: {sensor_frame: frame_name, data_type: LaserScan, topic: topic_name, marking: true, clearing: true}
- point_cloud_sensor: {sensor_frame: frame_name, data_type: PointCloud, topic: topic_name, marking: true, clearing: true}
详细解析以上配置文件的内容:
[html] view plain copy 
- obstacle_range: 2.5
- raytrace_range: 3.0
这两个参数用来设置代价地图中障碍物的相关阈值。obstacle_range参数用来设置机器人检测障碍物的最大范围,设置为2.5意为在2.5米范围内检测到的障碍信息,才会在地图中进行更新。raytrace_range参数用来设置机器人检测自由空间的最大范围,设置为3.0意为在3米范围内,机器人将根据传感器的信息,清除范围内的自由空间。
[html] view plain copy 
- footprint: [[x0, y0], [x1, y1], … [xn, yn]]
- #robot_radius: ir_of_robot
- inflation_radius: 0.55
这些参数用来设置机器人在二维地图上的占用面积,如果机器人外形是圆形,则需要设置机器人的外形半径。所有参数以机器人的中心作为坐标(0,0)点。inflation_radius参数是设置障碍物的膨胀参数,也就是机器人应该与障碍物保持的最小安全距离,这里设置为0.55意为为机器人规划的路径应该与机器人保持0.55米以上的安全距离。
[html] view plain copy 
- observation_sources: laser_scan_sensorpoint_cloud_sensor
observation_sources参数列出了代价地图需要关注的所有传感器信息,每一个传感器信息都将在后边列出详细信息。
[html] view plain copy 
- laser_scan_sensor: {sensor_frame: frame_name, data_type:LaserScan, topic: topic_name, marking: true, clearing: true}
以激光雷达为例,sensor_frame标识传感器的参考系名称,data_type表示激光数据或者点云数据使用的消息类型,topic_name表示传感器发布的话题名称,而marking和clearing参数用来表示是否需要使用传感器的实时信息来添加或清楚代价地图中的障碍物信息。
(2)全局规划配置文件(Global Configuration (global_costmap))
全局规划配置文件用来存储用于全局代价地图的配置参数,我们使用global_costmap_params.yaml来命名,内容如下:
[html] view plain copy 
- global_costmap:
- global_frame: /map
- robot_base_frame: base_link
- update_frequency: 5.0
- static_map:true
global_frame参数用来表示全局代价地图需要在那个参考系下运行,这里我们选择了map这个参考系。robot_base_frame参数表示代价地图可以参考的机器人本体的参考系。update_frequency参数绝地全局地图信息更新的频率,单位是Hz。static_map参数决定代价地图是否需要根据map_server提供的地图信息进行初始化,如果你不需要使用已有的地图或者map_server,最好将该参数设置为false。
(3)本地规划配置文件(Local Configuration (local_costmap))
本地规划配置文件用来存储用于本地代价地图的配置参数,命名为local_costmap_params.yaml,内容如下:
[html] view plain copy 
- local_costmap:
- global_frame: odom
- robot_base_frame: base_link
- update_frequency: 5.0
- publish_frequency: 2.0
- static_map:false
- rolling_window: true
- width: 6.0
- height: 6.0
- resolution:0.05
“global_frame”, “robot_base_frame”,“update_frequency”, 和 “static_map"参数的意义与全局规划配置文件中的参数相同。publish_frequency设置代价地图发布可视化信息的频率,单位是Hz。rolling_window参数是用来设置在机器人移动过程中是否需要滚动窗口,以保持机器人处于中心位置。“width,” “height,” 和"resolution” 设置设置代价地图长(米)、高(米)和分辨率(米/格)。分辨率可以设置的与静态地图不同,但是一般情况下两者是相同的。